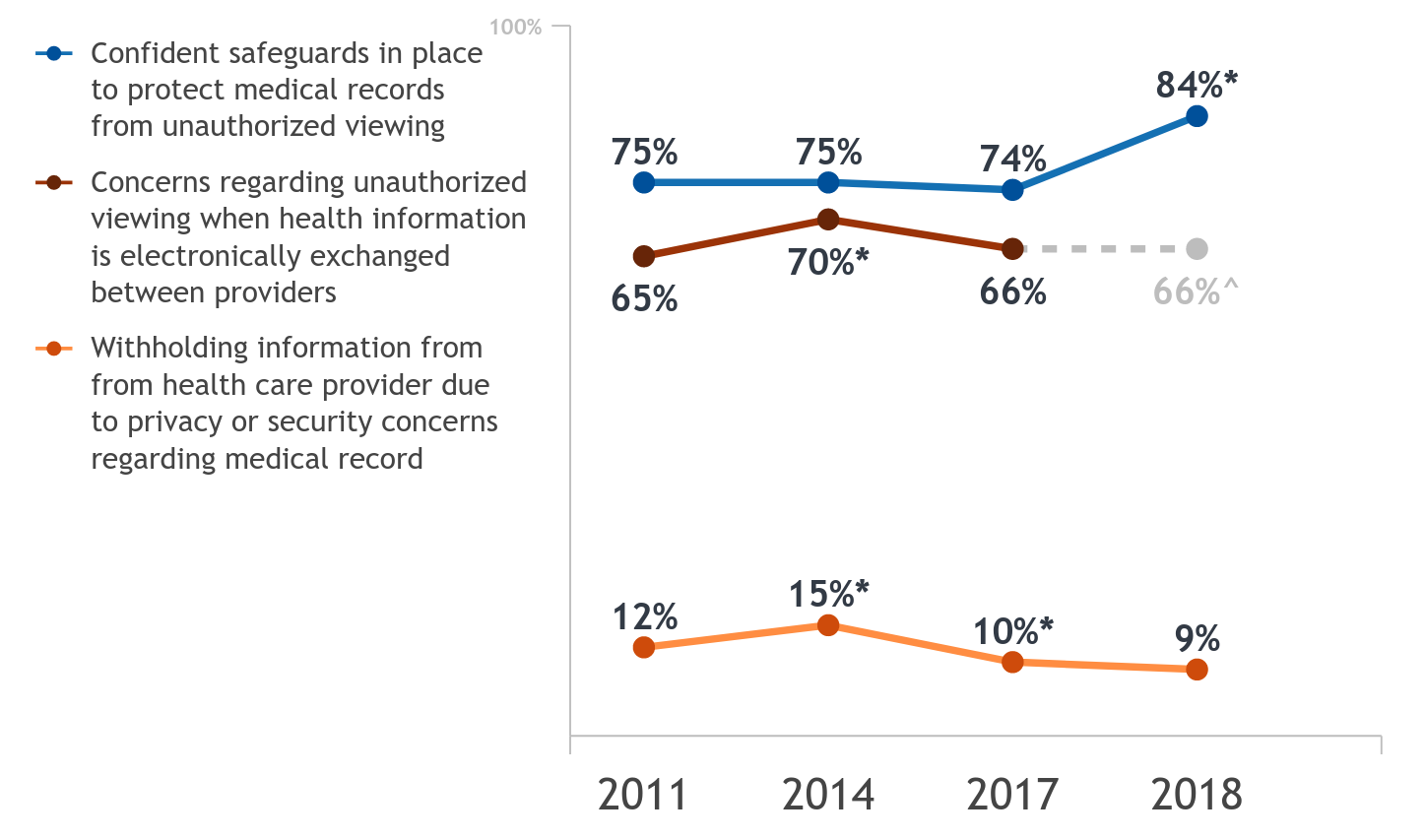
A majority of individuals (84%) are confident their medical records are safe from unauthorized viewing, but have concerns (66%) when health information is electronically exchanged. More individuals are now confident their records are safe from…
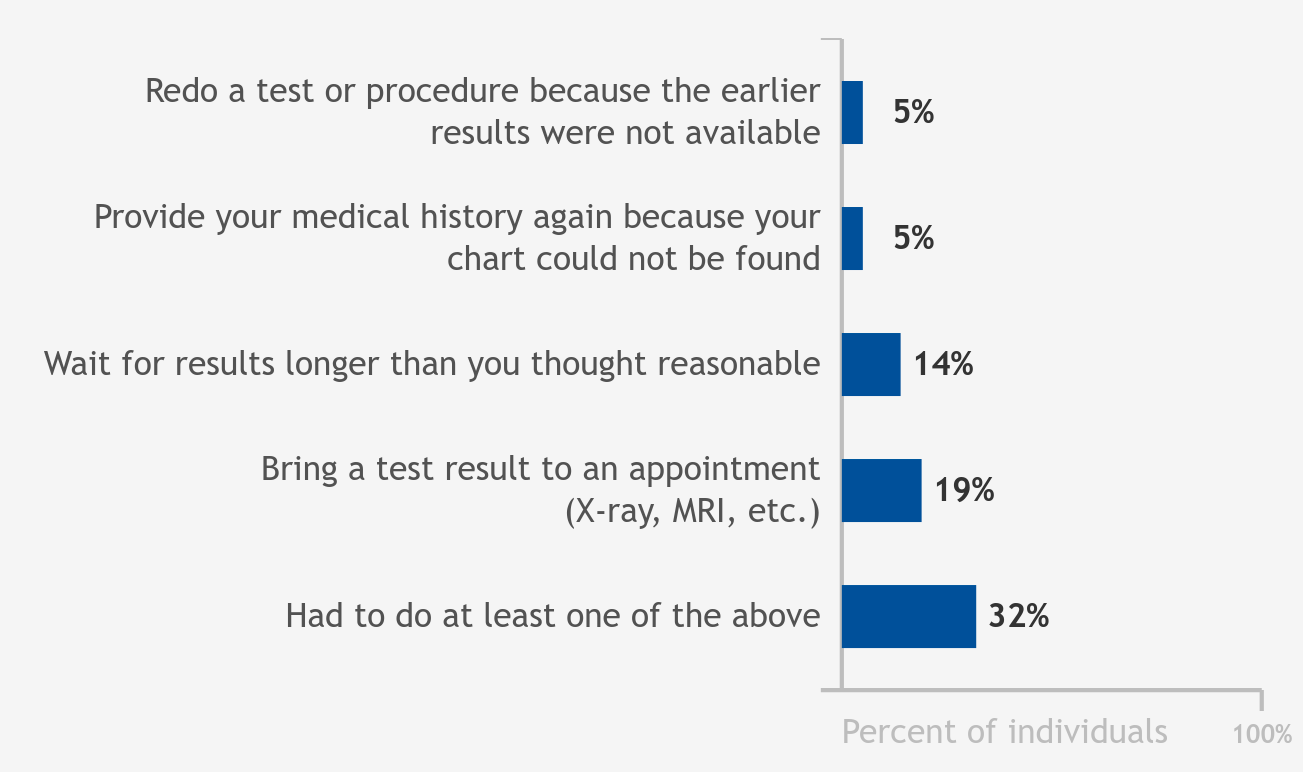
Eight-one percent of individuals went to a health care provider at least once within the past year. Overall, 32 percent of individuals who went to a doctor in the past 12 months reported experiencing a gap in information exchange. About 1 in 20…
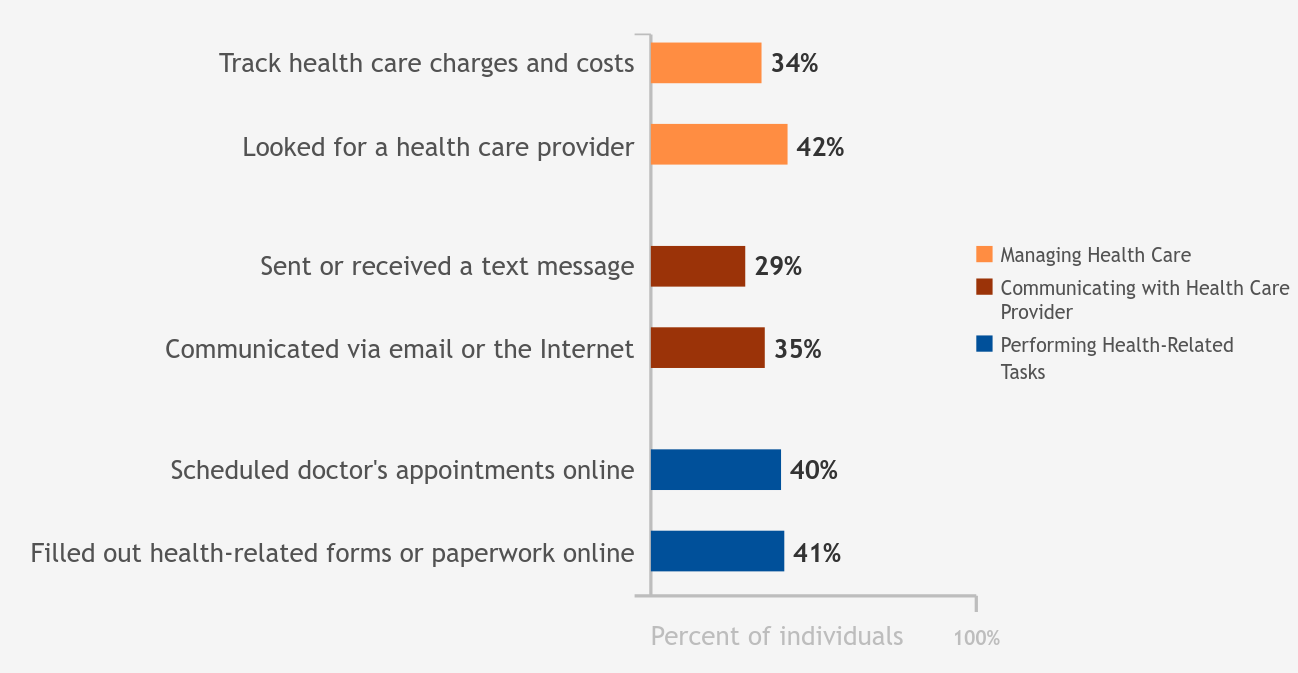
Overall, 1 in 3 individuals tracked health care charges and costs with a computer, smartphone, or other electronic means in the past 12 months. About 4 in 10 individuals filled out paperwork related to their health care or made health care appointments…

In 2015, 64% of physicians had an electronic health record (EHR) with the capability to exchange secure messages with patients, <br/>. Furthermore, 63% of physicians had the capability for their patients to electronically view their medical record…

Patient engagement EHR functionalities became more prevalent in U.S. hospitals from 2013 to 2015. The percentage of hospitals that provide patients the ability to view, download, and transmit their health records online accelerated from 2013 to 2015,…
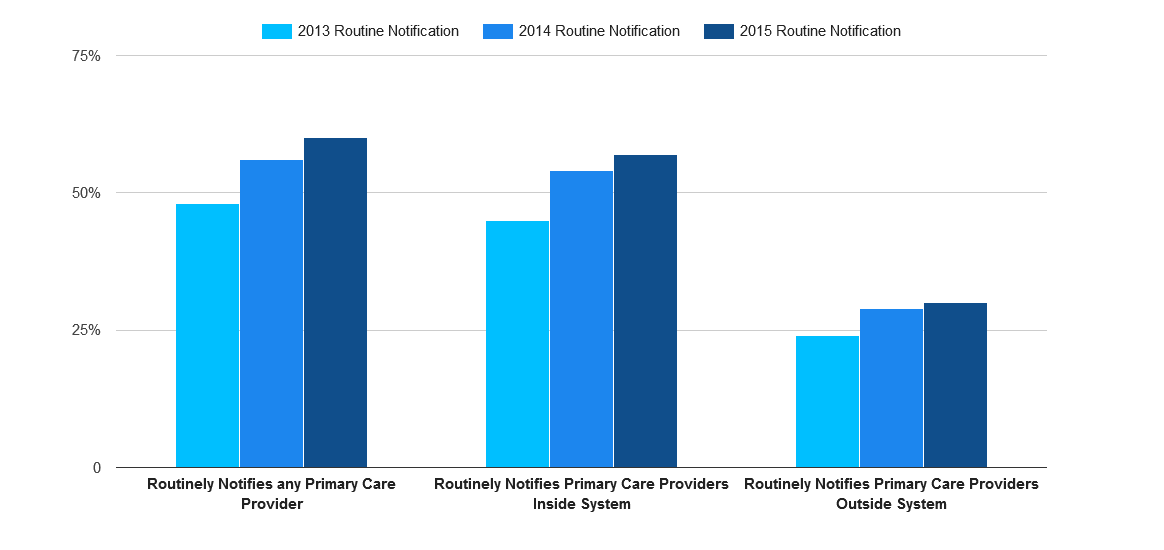
Three in five non-federal acute care hospitals routinely electronically notify a patient's primary care provider upon his entry to the hospital's emergency department - an over 50 percent increase since 2012. Fifty-seven percent of all…
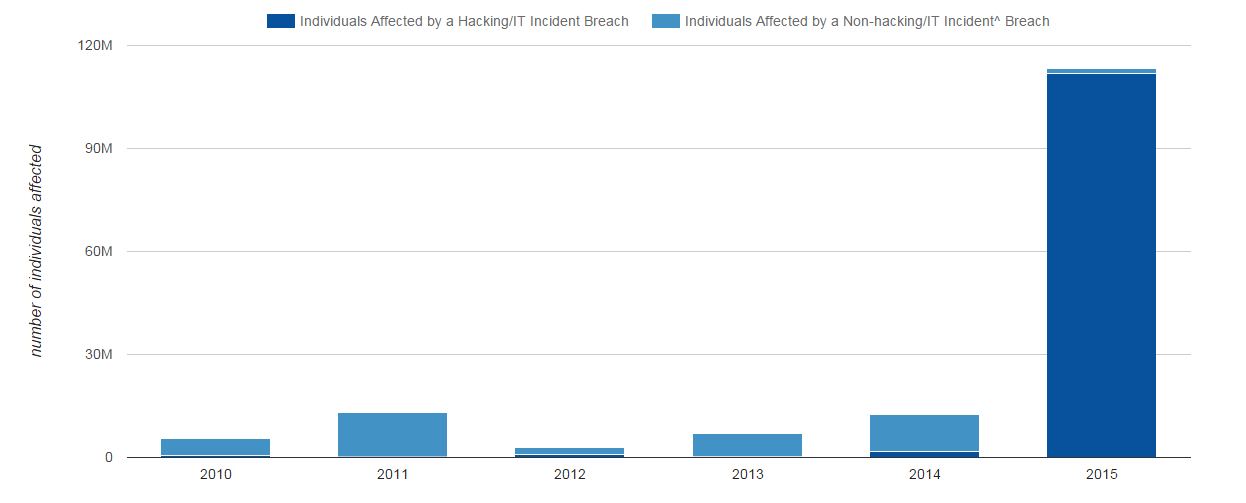
Based upon data collected by the HHS Office for Civil Rights, as of February 1, 2016, protected health information breaches affected over 113 million individuals in 2015. In 2015, hacking incidents comprised nearly 99% of all individuals affected by…
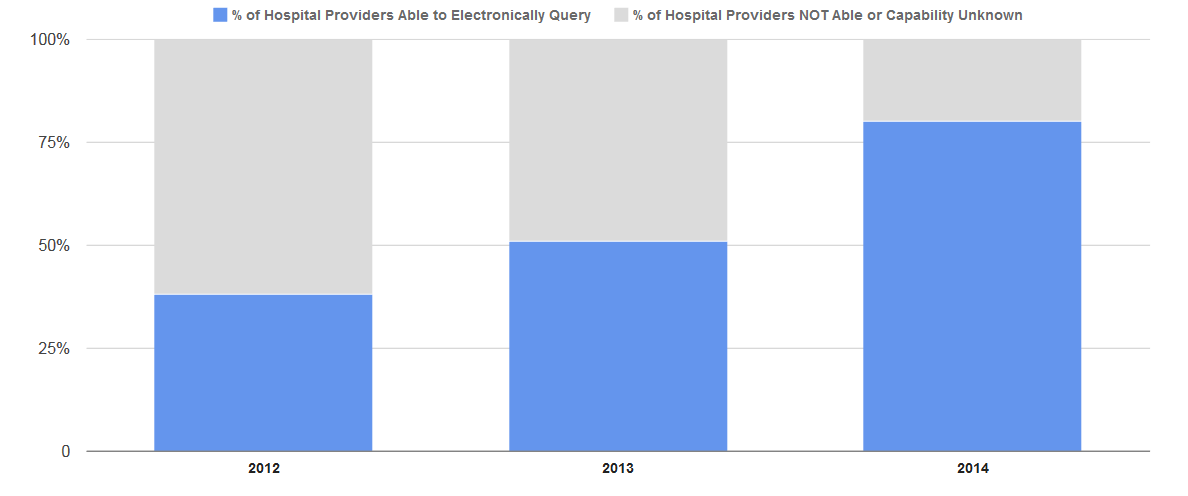
As of 2014, 80 percent of non-federal acute care hospitals have the capability to electronically query patient health information from external sources, an over 30 percentage point increase from 2013. In 2014, 48 percent of hospitals routinely queried…
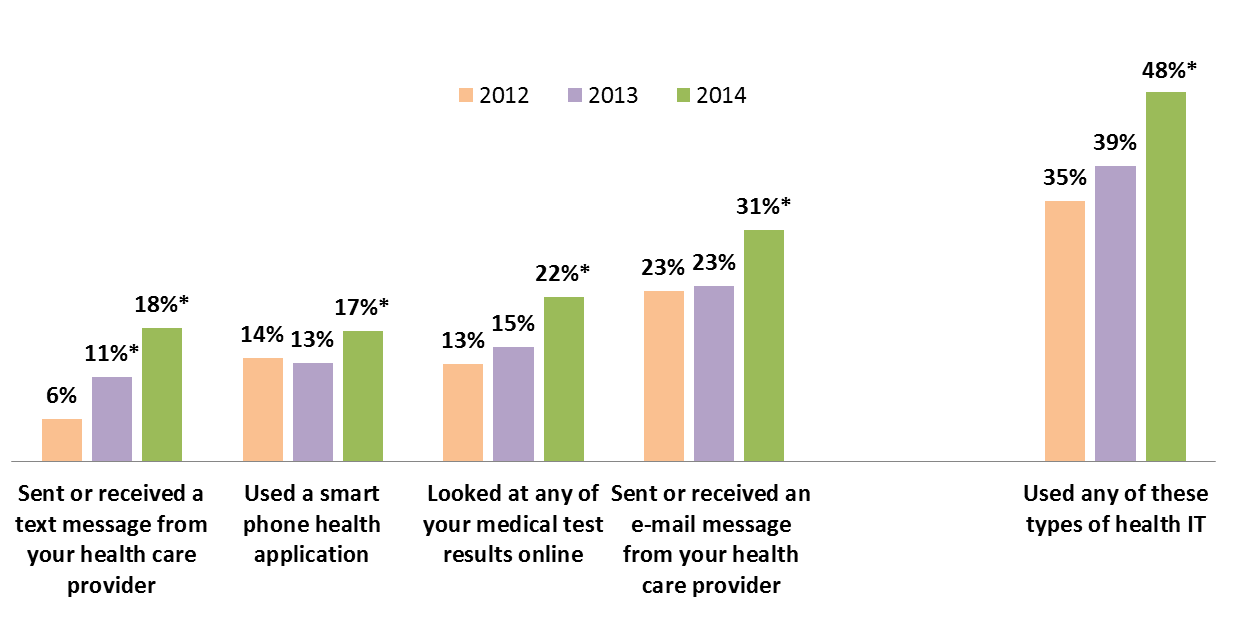
Individuals use of certain types of information technology to interact with their health care provider, view their personal health information, and track their health and wellness grew significantly between 2013 and 2014. The percent of individuals who…
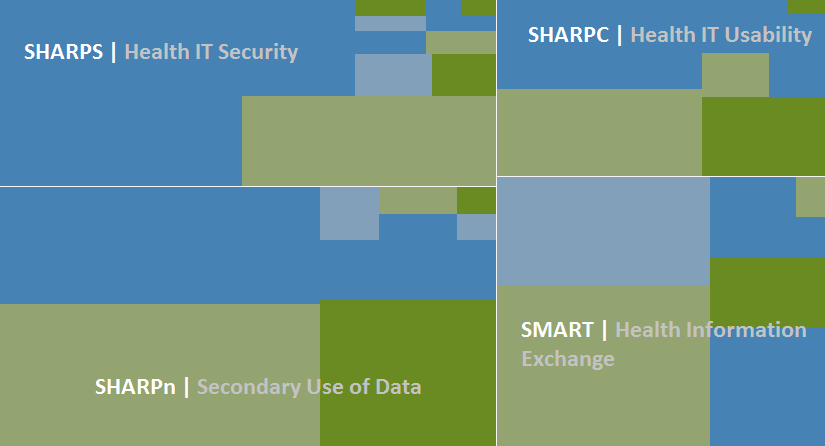
The Office of the National Coordinator for Health IT established the SHARP program to support innovative research and to address well-documented problems that impede the adoption and use of health IT. The SHARP program covers four subject areas:
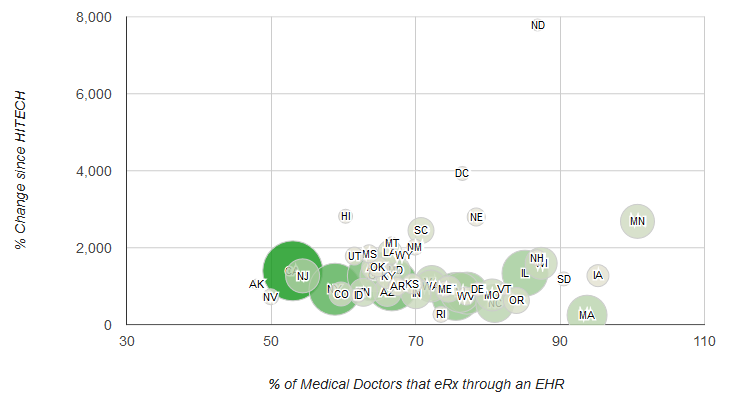
In December 2008, less than two months before the passage of the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act, fewer than 7% of all U.S. medical doctors electronically prescribed (e-prescribe) patient medications through an…
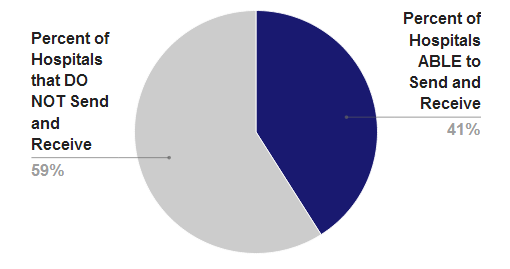
Approximately 4 in 10 hospitals (41%) report that providers at the hospital are able to send and receive secure electronic messages containing patient health information (e.g., medications) to and from sources outside of the organization or hospital…
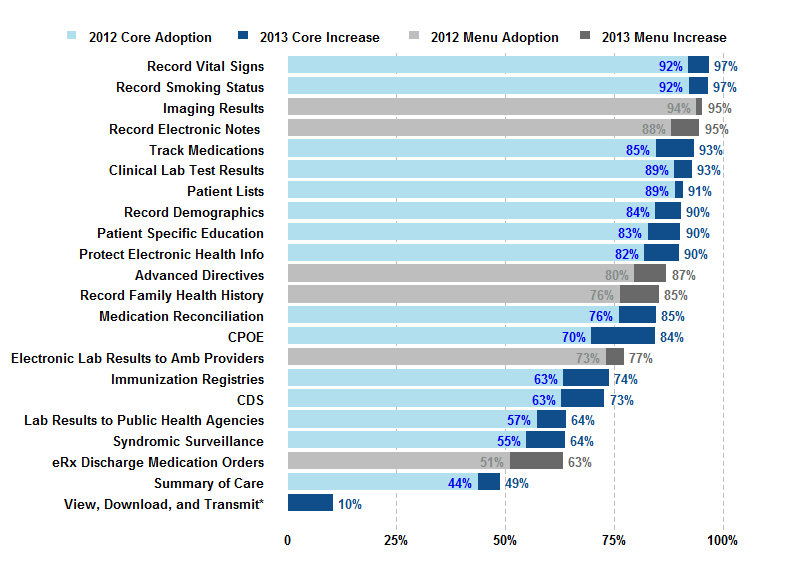
Stage Two of the Meaningful Use program consists of 22 core and menu objectives. A subset of hospitals will be eligible to begin attesting to these Stage 2 objectives in 2014. In 2013, adoption rates for 20 of these objectives were over 60 percent.…

Stage 1 of the Meaningful Use program consists of 24 core and menu objectives. Hospitals began attesting to Stage 1 in 2011.
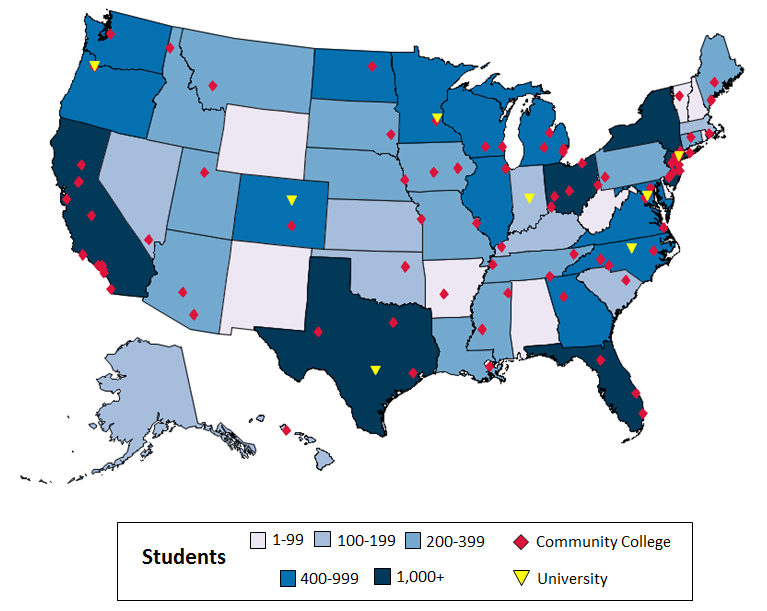
HITECH funded two distinct health IT workforce training programs: the University-Based Training Program and Community College Consortia Program. In total the two programs trained 21,437 students from all 50 states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico…
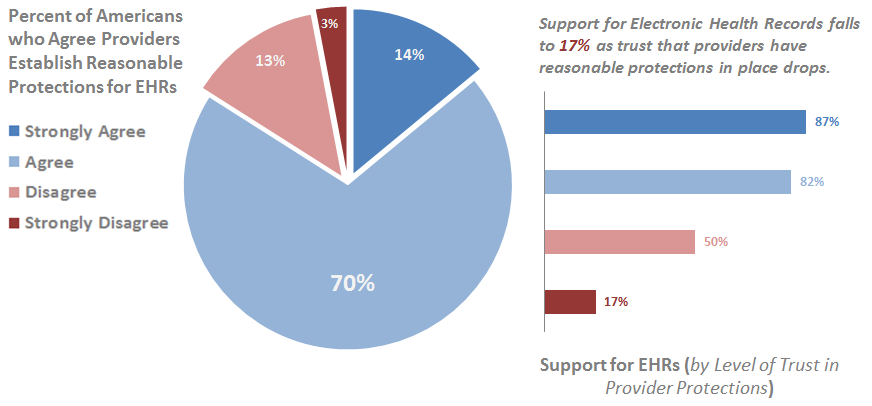
As the adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) and health information exchange (HIE) expands, and patient health information is increasingly stored and shared by providers electronically, it is important to monitor patient trust in providers'…
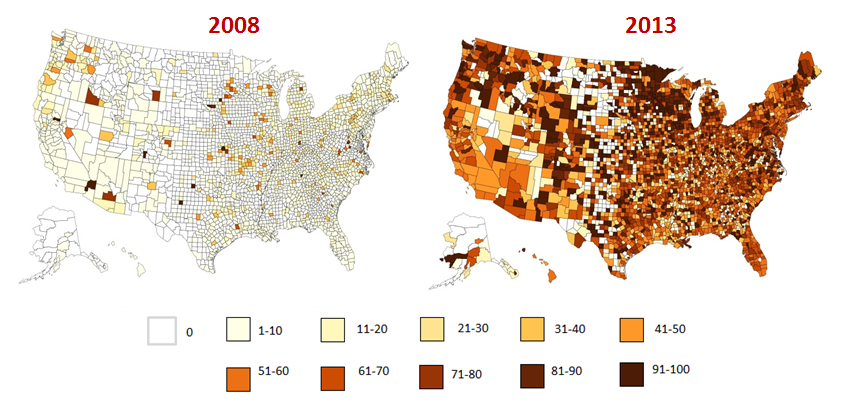
In the past five years, physician Electronic Health Record (EHR) adoption has surged, reaching all corners of the country. The percentage of physicians e-Prescribing via an EHR has accelerated from 7 percent in December 2008 to 66 percent as of December…
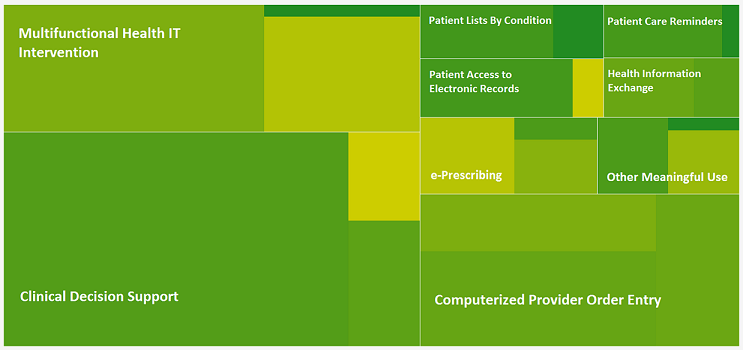
The 'Updated Systematic Review' reviews the January 2010 to August 2013 health IT literature to examine the effects of health IT across three aspects of care -- efficiency, quality, and safety. This report updates previous systematic reviews of…

